The Role of USB-A, USB-C, and Qi Charging: Where Power and Connectivity Are Headed

Introduction
In just a few short decades, the Universal Serial Bus—better known as USB—has completely changed the way we power and connect our devices. From transferring files between computers to charging phones, tablets, and headphones, USB has become the invisible backbone of modern technology.
Yet not all USB connections are the same. Two versions dominate today’s market: USB-A and USB-C. Add in the growing popularity of Qi wireless charging, and many consumers are left wondering: Which one do I actually need? Will USB-A disappear? Is USB-C the future? And how does wireless charging fit into all of this?
This article takes a deep dive into USB-A, USB-C, and Qi charging—covering their differences, advantages, disadvantages, and the direction trends are heading.
1. What Is USB-A?
USB-A, the rectangular connector most people have known for years, is the original and most widely used USB standard.
- Design: Large, flat, and rectangular.
- Compatibility: Found on desktops, laptops, power adapters, TVs, gaming consoles, and countless other devices.
- History: Launched in the mid-1990s, it became the universal connector for keyboards, mice, printers, flash drives, and phone chargers.
USB-A’s biggest strength has always been standardization. For nearly 20 years, if you had a USB device, it almost always plugged into a USB-A port.
But USB-A does have limitations:
- It only plugs in one way.
- Its size prevents it from being used in ultra-thin devices.
- Data transfer and power delivery have been capped compared to newer standards.
2. What Is USB-C?
USB-C is the newer, smaller, and more versatile connector that is rapidly replacing USB-A in phones, laptops, and accessories.
- Design: Small, symmetrical oval shape that works in either orientation.
- Speed: Supports faster data transfer rates (USB 3.2, USB4, Thunderbolt 4).
- Power: Can deliver much higher wattage (up to 240W with USB PD 3.1).
- Universality: One connector can do it all—charging, data transfer, video output, and networking.
The biggest selling point of USB-C is its flexibility and speed.
3. Key Differences Between USB-A and USB-C
| Feature | USB-A | USB-C |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Large, rectangular | Small, reversible oval |
| Ease of Use | One-way only | Works both ways |
| Data Transfer | Slower (up to 5 Gbps) | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Power Delivery | Limited (up to 12–15W) | Up to 240W |
| Use Cases | Legacy devices | Modern devices |
| Future Outlook | Slowly phased out | Expected universal standard |
4. Will USB-C Replace USB-A Entirely?
The short answer: Yes, but not overnight.
- USB-C is already standard on flagship smartphones.
- Most new laptops use USB-C, dropping USB-A.
- The EU now requires USB-C on all smartphones by the end of 2024.
That said, USB-A isn’t disappearing tomorrow:
- Billions of devices still rely on USB-A.
- Many low-cost accessories still use USB-A.
- Tech transitions often take a decade or more.
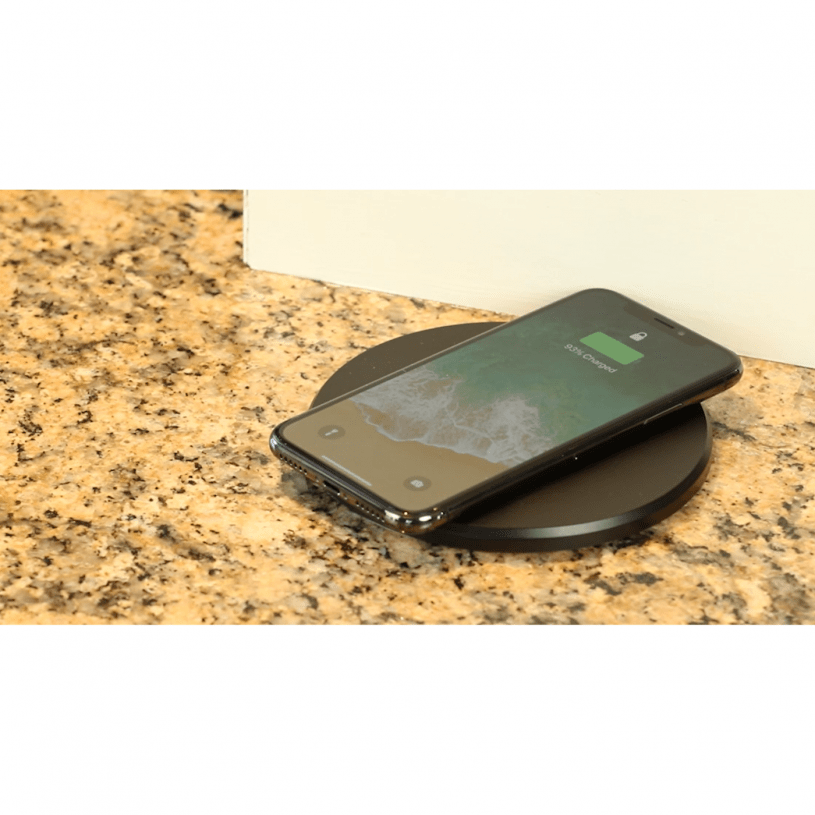
5. Where Does Qi Wireless Charging Fit In?
Qi is the standard for wireless charging used in most modern smartphones, earbuds, and watches.
- How it Works: Uses electromagnetic induction.
- Compatibility: Nearly all wireless-capable devices support Qi.
- Connection Point: Charging pads plug into USB-A or USB-C adapters.
Important: A Qi-enabled device doesn’t care if the pad is powered by USB-A or USB-C—the difference is speed.
6. Pros and Cons of Qi Wireless Charging
Pros:
- Convenience: No cables, just drop and go.
- Universal: One pad works with many devices.
- Reduced Wear: No ports to damage.
- Safety: Built-in protections.
Cons:
- Speed: Slower than wired charging.
- Heat: Can affect battery health.
- Placement: Must align correctly.
- Efficiency: More energy loss.
7. Current Trends in Charging and Connectivity
1. USB-C becoming the global standard.
2. Faster Power Delivery (USB-C PD).
3. Widespread Qi adoption.
4. Hybrid solutions (USB-A + USB-C + Qi).
5. Sustainability and reduced e-waste.
8. The Road Ahead: What Should Consumers Expect?
- Short-Term (2025–2027): Both A and C common. Hybrid solutions dominate.
- Medium-Term (2028–2030): USB-C dominates, USB-A lingers.
- Long-Term (2030+): USB-C + Qi remain primary methods. USB-A becomes obsolete.
9. Final Thoughts
USB-C is the future—it’s faster, universal, and versatile. USB-A will fade gradually, while Qi wireless charging grows in convenience but won’t fully replace wired solutions anytime soon.
Consumers should look for hybrid solutions that provide USB-A, USB-C, and Qi support to cover both current and future needs.
An Example of a Hybrid Charging Station
While USB-A, USB-C, and Qi wireless charging each have their strengths, modern solutions often combine them all into one convenient device. These hybrid charging stations allow you to plug in legacy devices, take advantage of high-speed USB-C charging, and enjoy the convenience of wireless Qi pads—all in the same outlet.
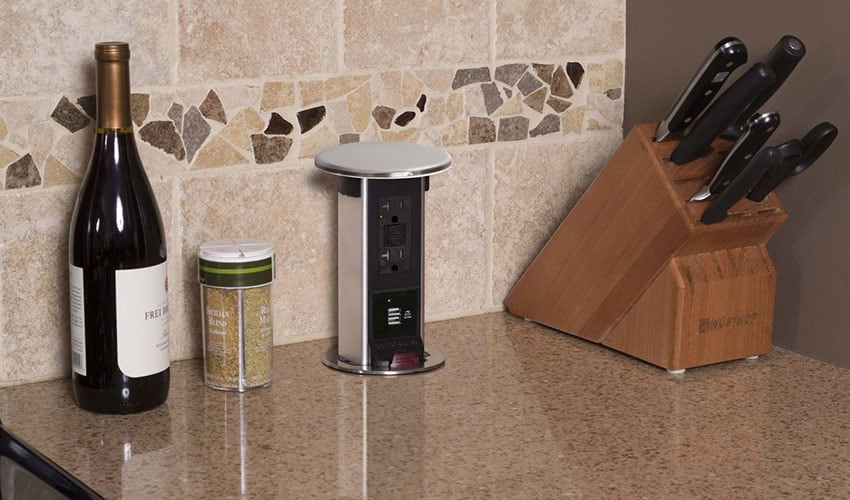

Shown here is Lew Electric’s PUR Series pop-up outlet. This hybrid charging station integrates USB-A, USB-C, and a Qi wireless charging pad right into the cover. It’s an ideal solution for modern kitchens, office spaces, or anywhere families and professionals need flexible, future-ready power access.
Learn more here: https://www.lewelectric.com/kitchen-countertop/pur-series/pur-series-wireless-charging-cover/
Blog
Latest Insights and Trends
Explore our latest blog posts on electrical solutions.
PVC vs. Metal Floor Boxes: What Inspectors Actually Care About
Choosing between PVC and metal floor boxes often sparks debate on job sites

Where Floor Boxes Make Sense in Commercial Spaces
Offices, Retail, Hospitality, and Beyond In commercial environments, electr

Where Should Floor Boxes Be Placed in a Living Room?
Practical Guidelines for Comfort, Safety, and Design Living rooms have evo
