Understanding IP Ratings: What They Mean and Why They Matter
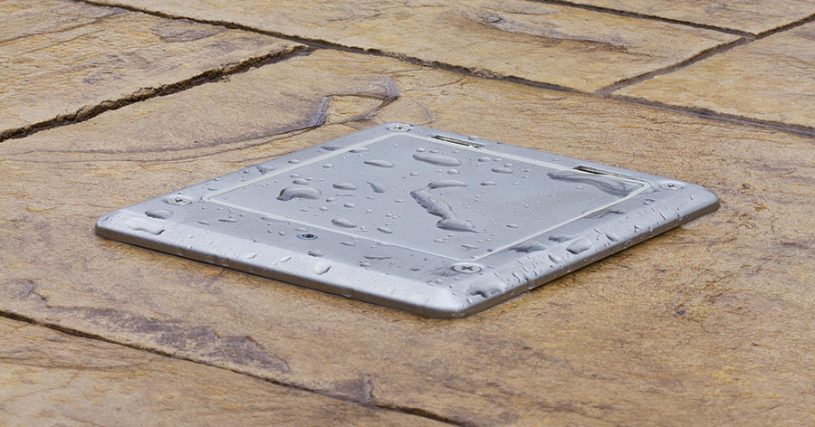

If you’ve ever shopped for outdoor lighting, electrical equipment, smartphones, or even floor boxes, chances are you’ve come across a mysterious code like IP44, IP65, or IP68. These numbers are not random—they’re known as Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, and they play a crucial role in determining whether a product can withstand dust, dirt, and water.
Understanding IP ratings helps consumers, contractors, and facility managers choose the right equipment for the right environment. In this article, we’ll break down exactly what these ratings mean, how to interpret them, and why they’re essential when safety and durability are on the line.
What Is an IP Rating?
An IP rating, or Ingress Protection rating, is an international standard defined by the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) under standard IEC 60529. It classifies how well electrical enclosures protect against solids (like dust and dirt) and liquids (like rain, splashes, or submersion).
Each IP code consists of two digits:
- The first digit tells you how resistant the enclosure is to solids.
- The second digit tells you how resistant it is to liquids.
For example:
- IP44 = Protected against solid objects over 1 mm and splashing water from any direction.
- IP67 = Dust-tight and protected against immersion in water up to 1 meter for 30 minutes.
The higher the number, the greater the protection.
Why IP Ratings Exist
Before these standards were developed, manufacturers often used vague terms like “water-resistant” or “dustproof.” The problem? Those words can mean very different things. A product labeled “water-resistant” might survive a light rain shower, but it might fail instantly if sprayed with a hose.
The IP rating system eliminates that confusion by setting clear, test-based criteria. Products are tested in controlled environments to see exactly how much dust or water they can handle, and they’re given an official rating.
This consistency helps:
- Consumers know what to expect.
- Installers ensure code compliance.
- Manufacturers build products that meet international safety standards.
Breaking Down the IP Code
First Digit: Protection Against Solids (0–6)
0 – No protection
1 – Protection against objects larger than 50 mm (e.g., a hand)
2 – Protection against objects larger than 12.5 mm (e.g., a finger)
3 – Protection against objects larger than 2.5 mm (e.g., tools, thick wires)
4 – Protection against objects larger than 1 mm (e.g., screws, small wires)
5 – Dust-protected: not completely dust-tight, but enough to prevent interference
6 – Dust-tight: complete protection against dust ingress
Second Digit: Protection Against Liquids (0–9K)
0 – No protection
1 – Protection against vertically falling drops of water
2 – Protection against vertically falling water at a 15° tilt
3 – Protection against spraying water at up to 60°
4 – Protection against splashing water from any direction
5 – Protection against water jets from any direction
6 – Protection against powerful water jets or heavy seas
7 – Protection against immersion up to 1 meter for 30 minutes
8 – Protection against continuous immersion beyond 1 meter (depth specified by manufacturer)
9K – Protection against high-pressure, high-temperature water jets (common in automotive or industrial equipment)
Common IP Ratings Explained
Here are some ratings you’re most likely to see:
- IP44: Splash-proof. Common for bathroom lighting or outdoor wall lights under eaves.
- IP54: Dust-protected and splash-resistant. Good for workshops or partially covered outdoor areas.
- IP65: Dust-tight and resistant to water jets. Popular for outdoor floodlights or patio installations.
- IP66: Dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets. Often used in industrial environments.
- IP67: Dust-tight and can handle immersion in shallow water. Found in rugged smartphones, outdoor electrical boxes, and poolside installations.
- IP68: Dust-tight and safe for continuous immersion. Used in underwater lights, marine applications, or premium electronic devices.
- IP69K: The highest protection—dust-tight and resistant to high-pressure steam cleaning. Used in heavy-duty vehicles and food processing facilities.
Why IP Ratings Matter in the Real World
- Safety – Electricity and water don’t mix. Choosing the wrong protection level could lead to short circuits, shock hazards, or fires.
- Durability – Dust and water accelerate wear and tear. IP-rated products last longer, saving money in the long run.
- Compliance – Building codes often require specific IP ratings in certain areas. Installing the wrong product could result in failed inspections.
- Confidence – Homeowners and businesses gain peace of mind knowing their installations are tested for real-world conditions.
Industry Applications
Residential:
- Bathrooms: Fixtures near showers require IP44 or higher.
- Kitchens: Appliances near sinks benefit from splash protection.
- Outdoors: Patios and gardens often require IP65 or higher.
Commercial:
- Restaurants: Kitchens and bars need splash-resistant equipment.
- Retail: Outdoor signage requires high IP ratings.
- Offices: IP-rated floor boxes protect outlets from cleaning equipment.
Industrial:
- Factories: Dust-heavy environments often need IP5X or IP6X.
- Car Washes: Equipment requires IP66 or higher.
- Food Processing Plants: IP69K enclosures withstand high-pressure washdowns.
Consumer Electronics:
Smartphones, earbuds, and wearables often advertise IP67 or IP68 ratings.
IP Ratings vs. Other Labels
It’s easy to confuse IP ratings with other certifications:
- NEMA Ratings: Common in North America, covering broader categories including corrosion and construction.
- UL Listings: Ensure compliance with U.S. safety testing but don’t specify dust/water ingress.
- Marketing Terms: “Waterproof” or “weatherproof” are vague—always check the IP rating.
Limitations of IP Ratings
IP ratings don’t account for:
- Temperature extremes (freezing or overheating)
- Chemical resistance (chlorine, salt)
- Aging and wear of seals
- Pressure variations beyond lab-tested conditions
How to Choose the Right IP Rating
Ask yourself:
- Will it be indoors or outdoors?
- Exposed to splashes, jets, or immersion?
- Facing dust, dirt, or heavy cleaning?
- Does code require a minimum rating?
General guide:
- Bathrooms/Kitchens: IP44–IP55
- Outdoors: IP65–IP67
- Industrial Washdowns: IP66–IP69K
Looking Ahead: The Future of IP Ratings
With smart homes, wearable tech, and smart cities on the rise, IP ratings are becoming more critical. Manufacturers are innovating with nanocoatings, better gaskets, and sleeker designs that blend aesthetics with protection.
Final Takeaway
IP ratings aren’t just numbers—they’re the difference between safe, reliable products and potential hazards. Whether you’re installing outdoor lights, floor boxes, or buying a new smartphone, knowing how to interpret an IP rating gives you confidence and ensures long-term performance.
Next time you see IP65, IP67, or IP68, you’ll know exactly what it means—and why it matters.
Blog
Latest Insights and Trends
Explore our latest blog posts on electrical solutions.
PVC vs. Metal Floor Boxes: What Inspectors Actually Care About
Choosing between PVC and metal floor boxes often sparks debate on job sites

Where Floor Boxes Make Sense in Commercial Spaces
Offices, Retail, Hospitality, and Beyond In commercial environments, electr

Where Should Floor Boxes Be Placed in a Living Room?
Practical Guidelines for Comfort, Safety, and Design Living rooms have evo
